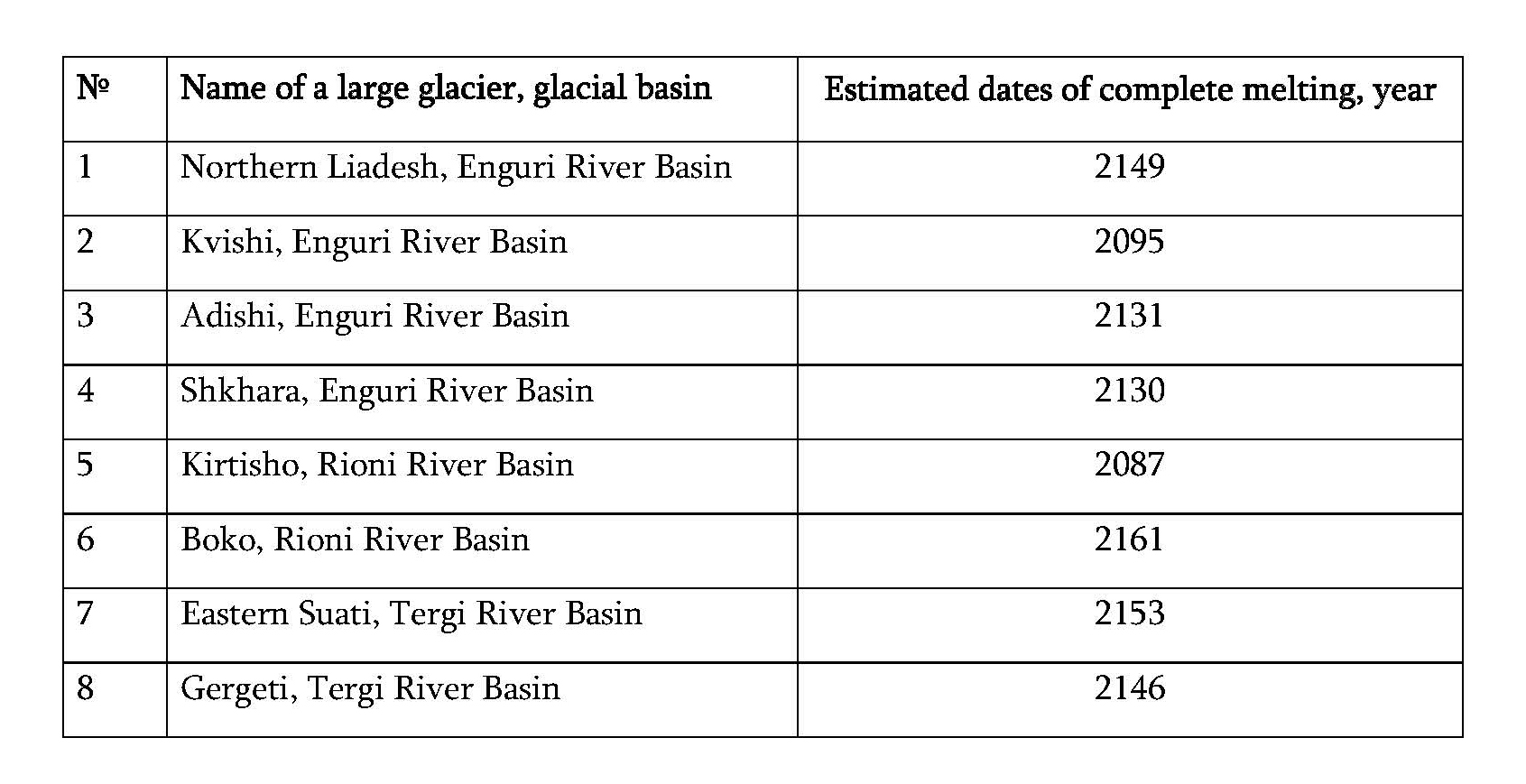
In western Georgia, only two, the Bzipi and Kelasuri basins, do not have large glaciers (only one small glacier has survived in the Khobistskali basin). To determine the dynamics of changes in the areas of glacial basins, specific processing of satellite data is required , which includes several stages. First, let's define the research area. Then, let's identify the glacial basins of these two rivers. To determine the area of glaciers, let's process satellite data, namely, determine the reflectivity of the earth's surface, make topographic corrections of the obtained results, and classify the so-called unsupervised data. After classification, it is possible to determine the total area of glaciers in a separate basin and its chronological change.
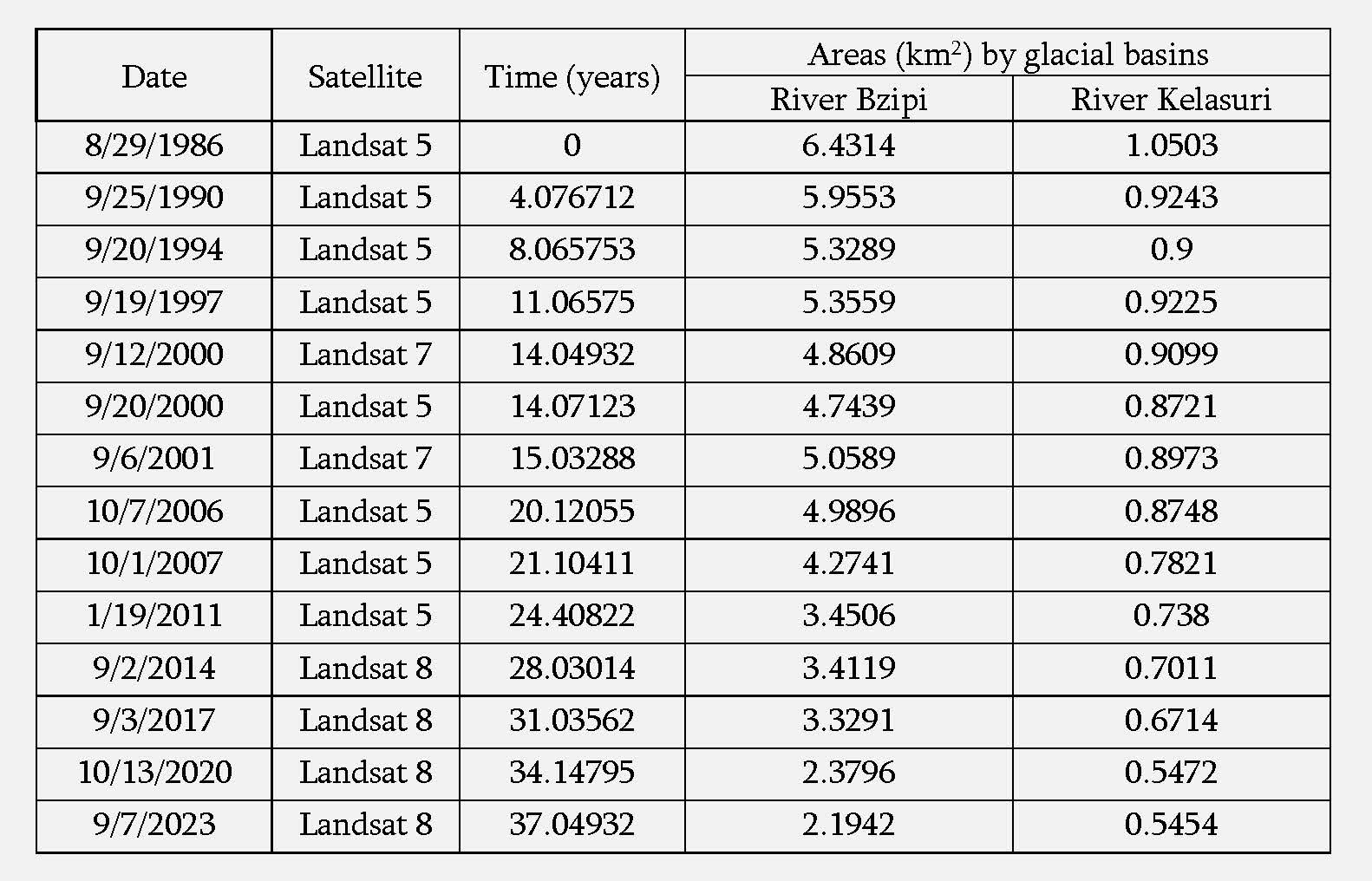
The dynamics of glacier change in the Bzifi and Kelasuri basins The analysis used data from Landsat 5, 7, and 8 satellites for the time interval from 1986 to 2023. Satellite data for fourteen different dates were available for this period. Table 6 shows the total areas of glaciers determined by the SRS by date.